Solution
Electric
natural gas
What’s e-NG?
Who can use e-NG?

Natural gas-run passenger and cargo ships can easily decarbonize by switching their fuel source to e-NG. Infrastructure and staff can all remain the same, and there’s no risk of service disruption due to a secure supply of e-NG.

e-NG can be used as a compressed natural gas drop-in fuel for trucking fleets that currently run on CNG. e-NG can also be reformed into green hydrogen for use in hydrogen combustion engines or hydrogen fuel cells.
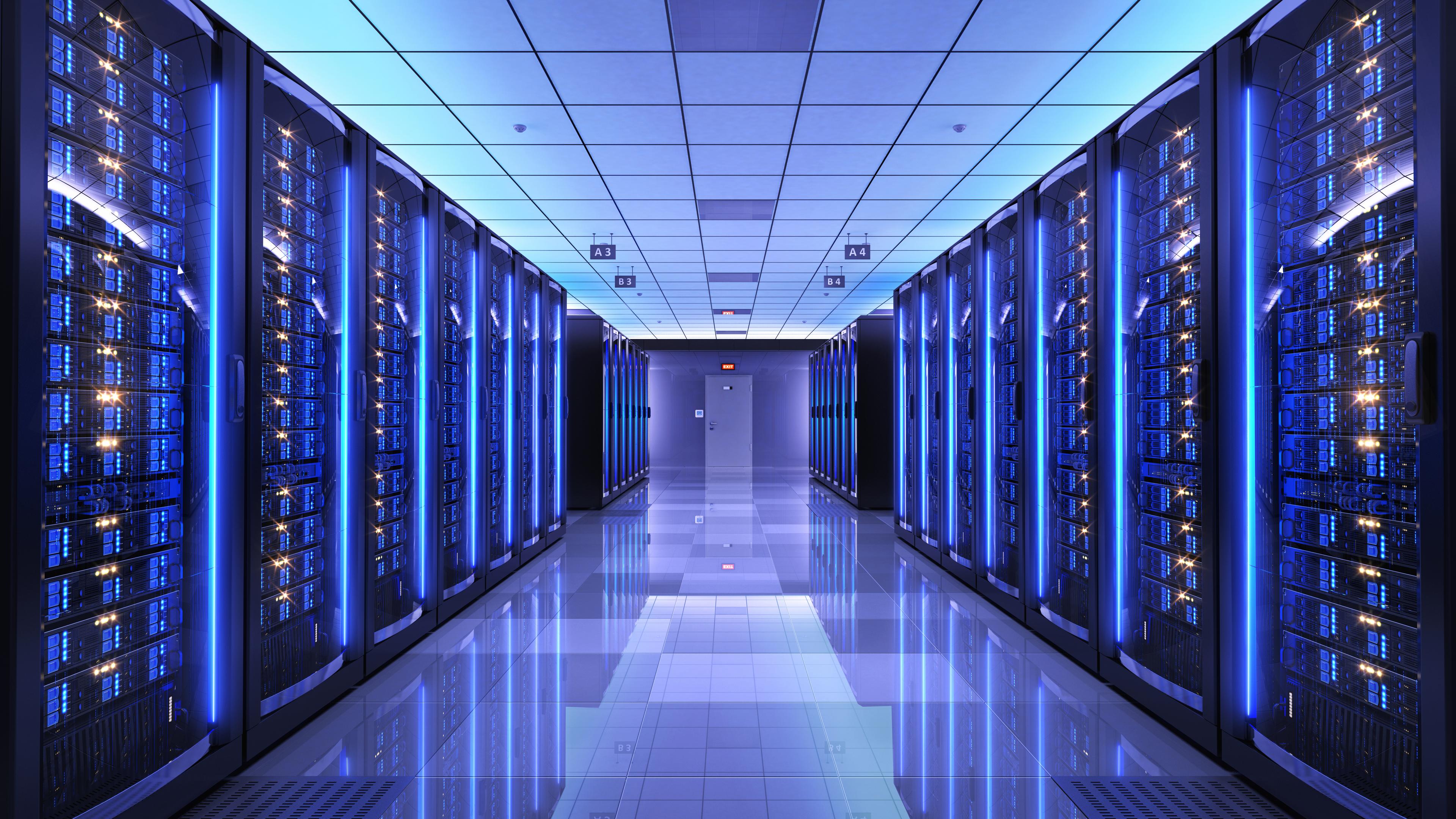

As AI’s energy needs soar, e-NG offers a path to decarbonize the data center operations. It can supply around-the-clock power at a potentially unlimited scale while seamless integrating with existing infrastructure. E-NG provides a reliable, scalable, “drop-in” solution for AI’s growing demands.
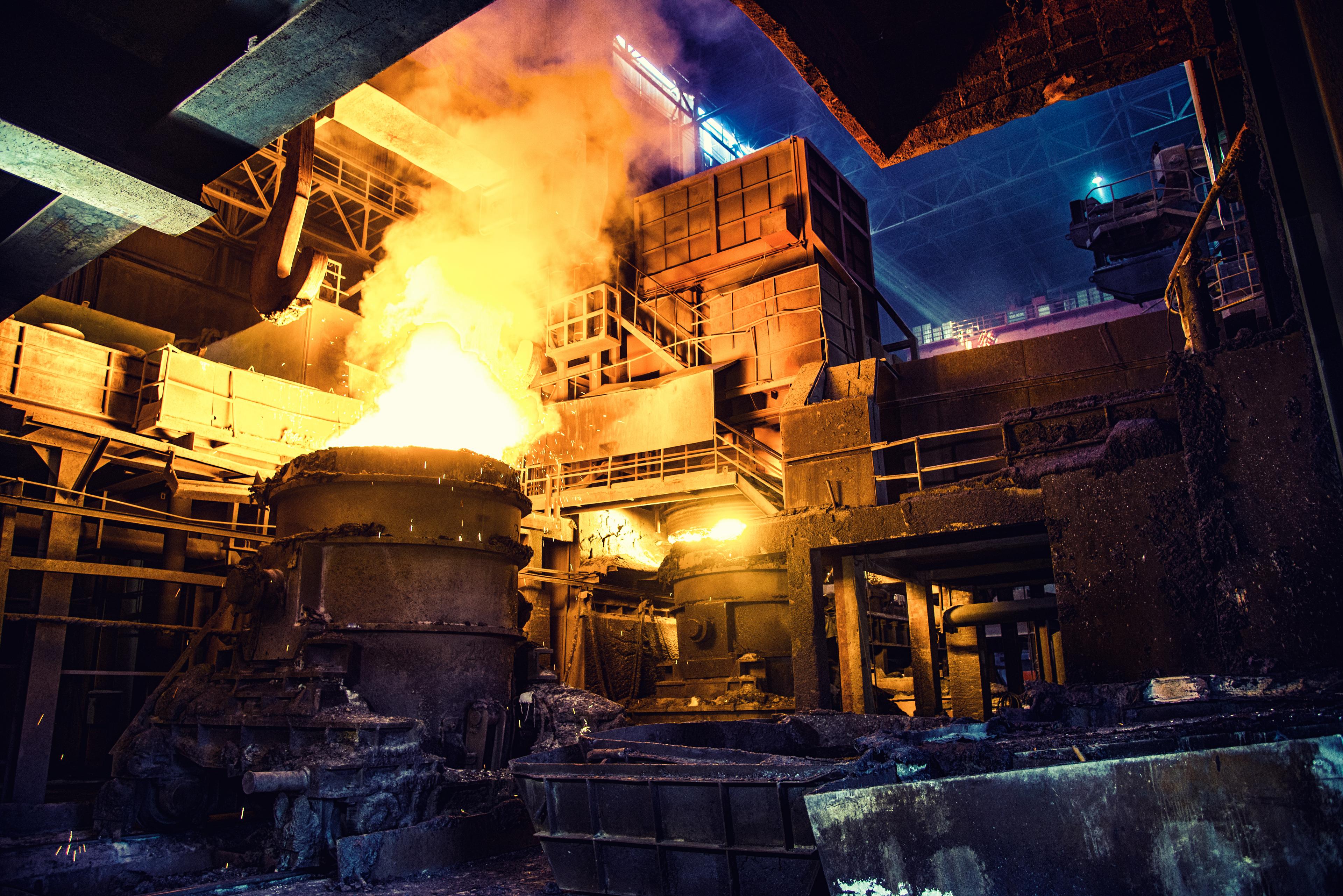

As it blends easily into the fuel mix with natural gas, commercial direct reduction plants (DRP) can use e-NG as a drop-in fuel to begin defossilization. Other plant processes heated with natural gas like the walking beam furnace can also be decarbonized by e-NG.
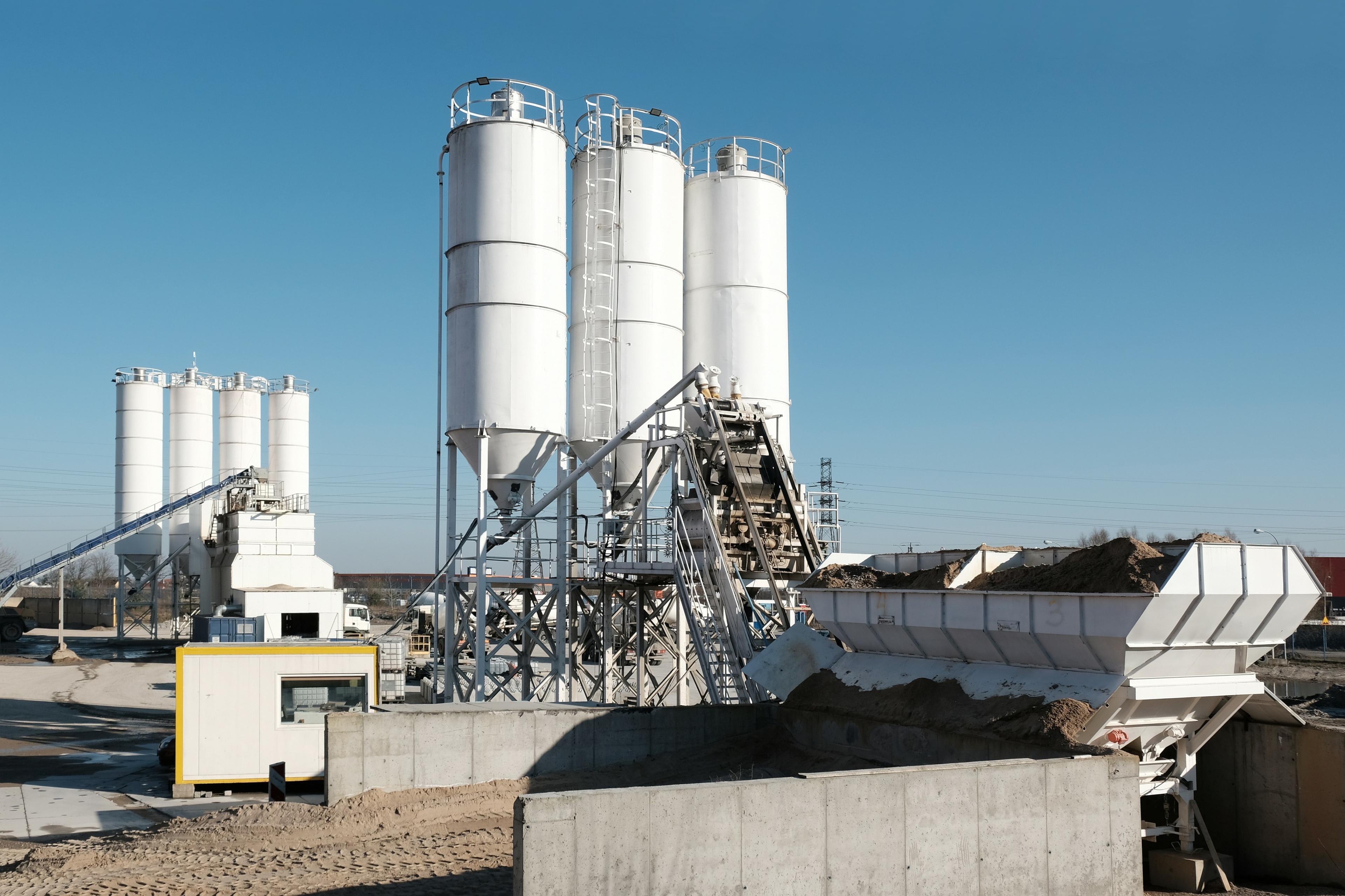

e-NG can directly replace fossil fuels used in cement production and abate emissions from fuel combustion. The glass industry can also blend e-NG into existing furnaces used for glass melting.
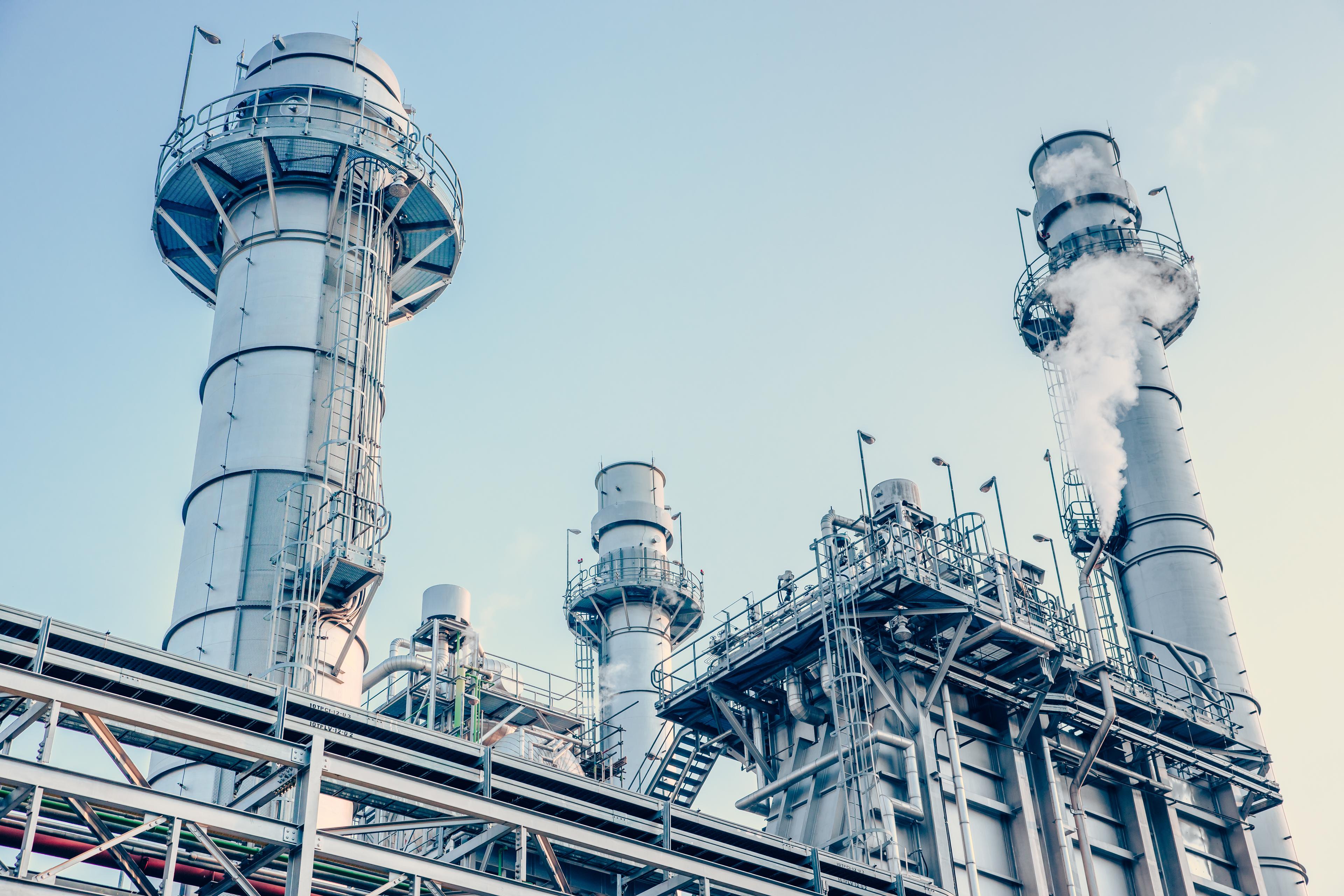

Natural gas is a vital feedstock in the chemical industry (e.g., for steam methane reformers and ammonia production). By using e-NG, these processes become decarbonized without requiring new investments. e-NG can also economically reduce emissions when replacing natural gas for power and heat generation in existing CHP systems.
Why your company should use e-NG

No new infrastructure needed

Scalable and flexible

Cost-effective

